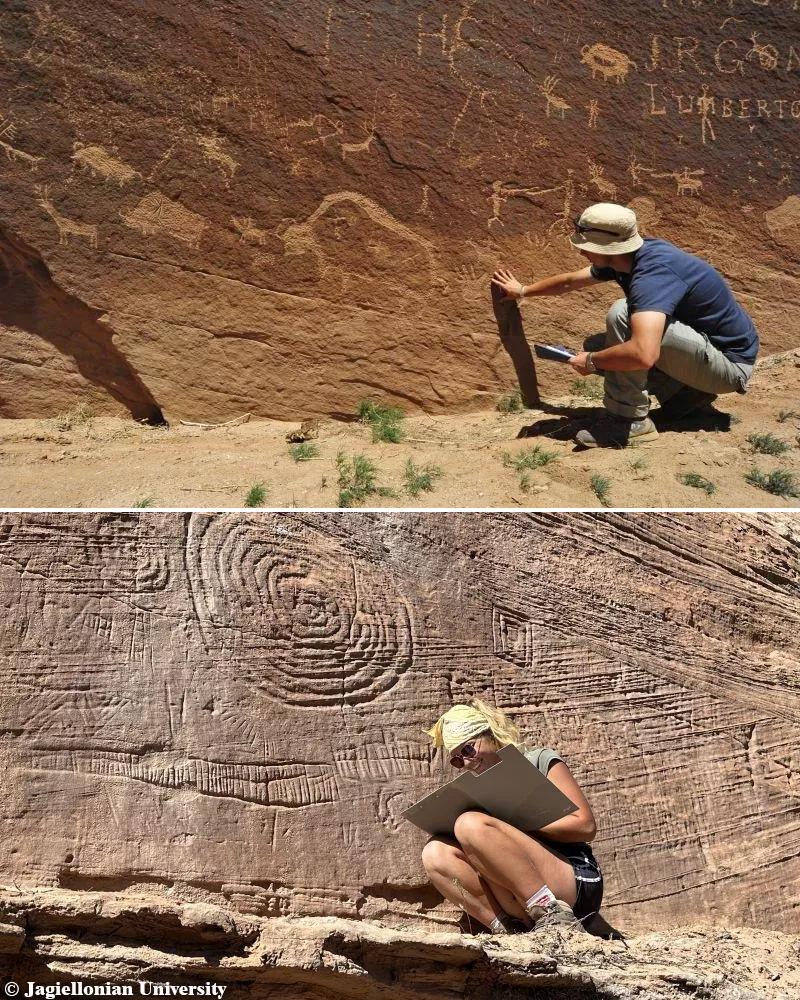
Endothermic Animal is the Greek word Endo meaning "inner/endogenous", the word therm meaning "temperature". Endothermic Animal is a technical term used to refer to organisms that maintain their body temperature entirely based on their surroundings.
Mechanism of action
Cold-blooded animals often produce heat through metabolism, and in extreme environmental conditions, they often adopt special mechanisms to survive. Cold-blooded animals have a large number of mitochondria compared to other warm-blooded species, which allow for an increased rate of fat and sugar metabolism. Accordingly, to maintain life, they need twice as much food as warm-blooded animals, which will help metabolism take place better.
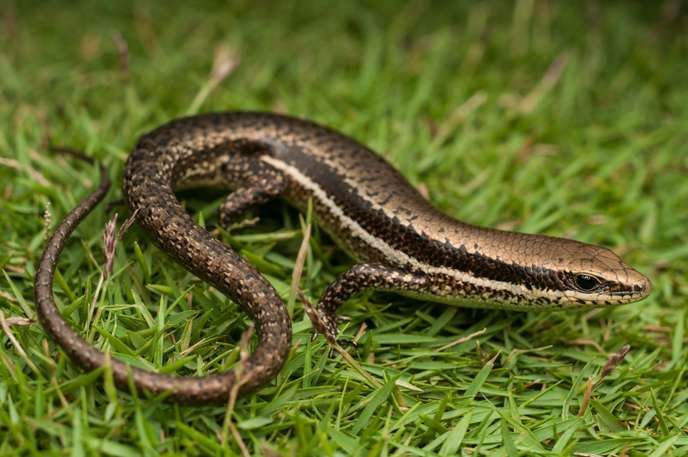


Endothermic animals adapt quite well to changes in outside temperature.
In nature, animals such as snakes, lizards, etc. will temporarily reduce their heat to close to the surrounding temperature to save energy. Biologically, this state is almost like a "coma" state, but if it lasts longer and is cyclical, it will be a hibernation process. Small animals like hummingbirds will significantly reduce their daily activity time, maintaining body temperature. Humans belong to the group of endothermic animals, but when we sleep, our metabolism decreases, the body temperature will drop by about 1 degree Celsius. In the human body, the brain produces about 16% of the total heat and about 2/ 3 the amount of heat generated during respiration and other metabolism of internal organs.
Classification method
Like warm-blooded animals, cold-blooded or endothermic animals are also divided into three types, including: Endothermic animals, ectothermic animals and slow metabolizing animals.
Endothermic animals are organisms that can maintain their body temperature over a wide range of temperatures.
Endothermic animals will be greatly affected by the external environment, such as sun, wind, snow, especially heat generated from the Sun.
In contrast to fast-metabolizing warm-blooded animals, slow-metabolizing animals are usually hibernating species, when the ambient temperature drops for a long time. Typically, there are bears, Poorwill birds, Red-eared turtles hibernating in the water, newts ...
The obvious advantage in ectothermic animals is that they are quite well adapted to changes in outside temperature. In addition, thermophilic individuals have a good immune system to fungal-related skin diseases, especially adult individuals. The change in temperature is also an evolutionary advantage of thermogenic organisms. above.
Because it uses a lot of energy for metabolism, this makes cold-blooded animals need a higher amount of food, the time of day activity is also limited, depends heavily on sunlight, when foraging. They also prefer waiting for prey to fall into a trap rather than putting themselves in a chase, thus consuming too much energy.